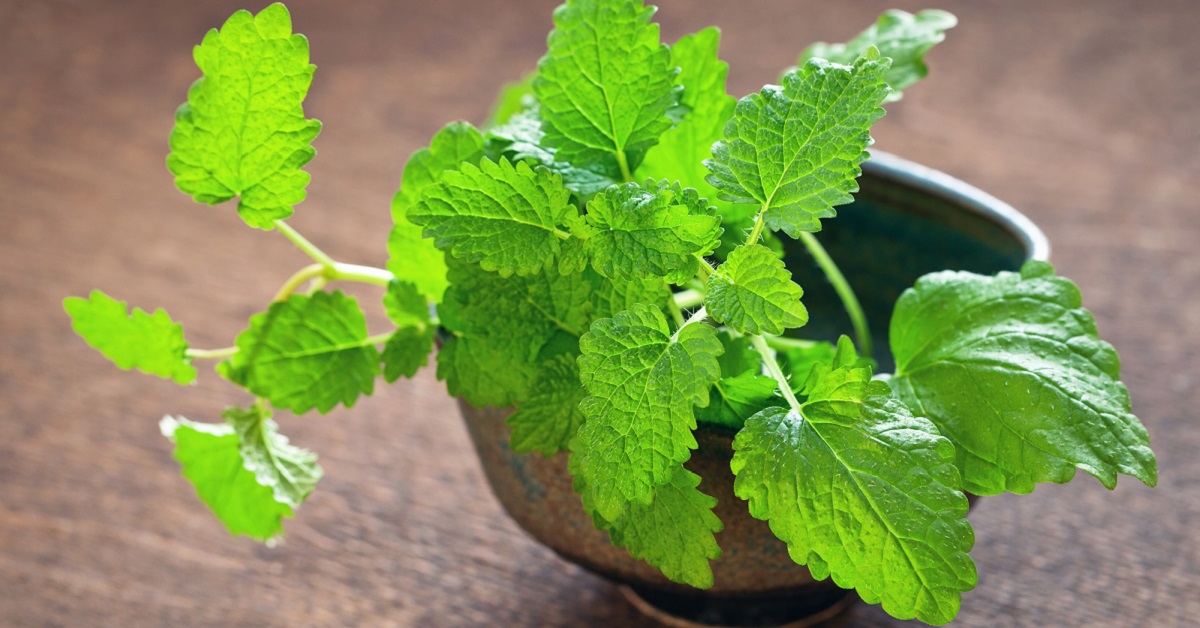
The latest research reveals that a little-known herb from the mint family can keep your memory in mint condition.
Tests in England show that people using this herb experience “improved memory performance and increased calmness.”1
And a laboratory study in Japan suggests this herb may increase neurotransmitters in the brain in a way that could lower the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.2
Let’s take a look at the new research on lemon balm…
One of the first recorded uses of lemon balm was to attract bees. Roman beekeepers rubbed it on their new hives to lure bee colonies to set up home and produce valuable honey.
Hundreds of years later, around the tenth century, medical folks in the Middle East gave lemon balm to patients to relieve melancholy and heart problems.
Today, researchers are learning how lemon balm can help preserve our cognitive abilities by supporting better brain health.
Protects Against Dementia Induced by Diabetes
One of the biggest health challenges we face today is the damage to the brain that results from having diabetes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 100 million Americans suffer type 2 diabetes or have prediabetes, defined as blood sugar control issues that can lead to diabetes.
And while having diabetes increases the chances that you may suffer Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia, lemon balm may help protect against these blood-sugar-induced cognitive disorders.3
Much of this research has focused on rosmarinic acid, a natural chemical found in lemon balm. Lab tests have found that this phytochemical can potentially reduce “learning and memory deficits induced by diabetes.”4 The tests also show that rosmarinic acid could protect the body’s neurons by increasing the activity of the body’s own antioxidants and helping to keep blood sugar under control.
A study at the University of Denver indicates that when combined with carnosic acid– a natural chemical found in rosemary– rosmarinic acid can protect neurons from being damaged by inflammation, while also keeping them safe from oxidative stress.5 Researchers concluded that these actions could help protect the brain against Alzheimer’s disease.
Fighting Damage from Environmental Toxins
Recent studies are also turning up other health benefits of rosmarinic acid that may be particularly important in our polluted modern world.
Lab tests demonstrate that this natural substance can help the body resist the harm we suffer from the plastic contamination that is entering our food, water and even our air. Some of the most widespread and problematic pollutants we are exposed to belong to a class of chemicals called phthalates – toxins that are used as solvents in cosmetics and added to packaging as plastic softeners (also called plasticizers).
When absorbed by the body, these chemicals act as endocrine disruptors, which means they interfere with the normal actions of hormones and the organs that secrete them.
But researchers in Asia have found that while phthalates can hamper thyroid function and cause cells in the thyroid to succumb to inflammation, rosmarinic acid can interrupt this destructive cycle, influencing immune cells in ways that lower inflammation and keeping thyroid cells from dying.6
Improves Mental and Emotional Health
Other areas of research into lemon balm and its natural chemicals have found that:
- Lemon balm can act as an antidepressant: A study in Italy shows that when combined with magnolia and L-theanine (an amino acid that modulates neurotransmitters), lemon balm can ease mood disorders.7
- Lemon balm can relieve stress: Tests in Australia demonstrate that lemon balm can reduce anxiety and lower levels of cortisol (a stress hormone).8
- Lemon balm can stop insomnia: Lemon balm improved sleep disorders such as insomnia and restless leg syndrome in a 2006 study. The most powerful results came about when researchers combined lemon balm with valerian root.9
One of the best aspects of lemon balm is its enjoyable odor and taste. In fact, many folks add lemon balm to entrees and salads. It also makes a refreshing lemon tea.
You can buy fresh lemon balm herb or get it as a tea, oil extract and supplement from healthfood stores and online. Plus, it’s fairly easy to grow lemon balm unless you live in a cold part of the world. In fact, it’s rather invasive and can take over your garden if you’re not careful!
Very few people experience any side effects from lemon balm, although there is a remote chance you could have an allergy. If you have diabetes, lemon balm might also lower your blood sugar so, in that case, keep an eye on your blood sugar levels if you use this herb.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12888775/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-45168-1
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23314404/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030439401630266X#!
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6278428/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32612006/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/6/1803/htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4245564/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944711306000250?via%3Dihub